#using the polynomial function to predict next year's stock performance
start = '2008-01-01'
end = '2018-01-01'
price_train = get_pricing('AAPL', fields='price', start_date=start, end_date=end)
start = '2008-01-01'
end = '2019-12-01'
price_test = get_pricing('AAPL', fields='price', start_date=start, end_date=end)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
polyfit_order = 2
def polyfit_training(N=polyfit_order):
x = np.arange(len(price_train))
c = np.polyfit(x, price_train.values, N)
y = np.zeros(len(price_train))
for i in range(0, N+1):
y += np.power(x,N-i)*c[i]
f = pd.Series(y, index=price_train.index, name='prediction order {} '.format(N))
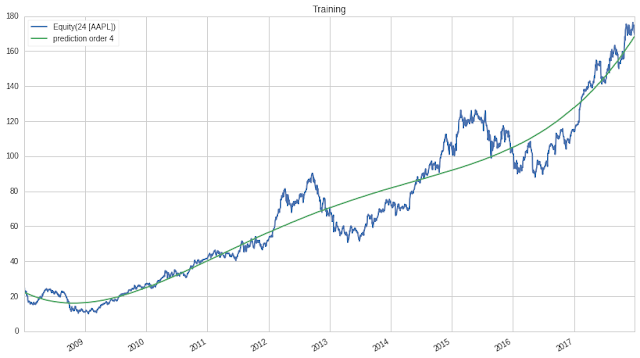
pd.concat([price_train, f], axis=1).plot()
plt.title('Training')
return c
def polyfit_prediction(N=polyfit_order):
c = polyfit_training(N)
x = np.arange(len(price_test))
y = np.zeros(len(price_test))
for i in range(0, N+1):
y += np.power(x,N-i)*c[i]
f = pd.Series(y, index=price_test.index, name='prediction order {} '.format(N))
return f
pd.concat([price_test, polyfit_prediction(4)], axis=1).plot()
plt.title('Prediction')
given apple 10 years performance(2008-2018), generate 4th order polynomial
using the polynomial to predict apple performance in 2019
prediction is higher than real price
pd.concat([price_test, polyfit_prediction(3)], axis=1).plot()
train 3rd order ployfit
prediction is lower than real price
train 3rd order polyfit for Deutsche Bank
predicted performance is worse than real
train 2nd order polyfit for Deutsche Bank
performance is close to real
2nd order IBM
5th order IBM
3rd order Exxon mobile
5th order Exxon mobile
http://chuanshuoge2.blogspot.com/2019/12/quotopian-lecture-polyfit.html















No comments:
Post a Comment